- Time:2024/07/15 Posted:Dongguan Jierui Hardware Technology Co., Ltd
In the fastener forming process, cold heading (extrusion) technology is a main processing technology, which belongs to the category of metal pressure processing. In production, at room temperature, external force is applied to the metal to form the metal in a predetermined mold. This method is usually called cold heading. In fact, the forming of any fastener is not only achieved by cold heading. In the cold heading process, in addition to upsetting deformation, it is also accompanied by positive and negative extrusion, compound extrusion, punching, rolling and other deformation methods. Therefore, the name of cold heading in production is just a habitual name. To be more precise, it should be called cold heading (extrusion).
Cold heading (extrusion) has many advantages, and it is suitable for mass production of fasteners. Its advantages can be summarized as follows:
High steel utilization rate. Cold heading (extrusion) is a method with little or no cutting. For example, when machining hexagonal bolts and cylindrical hexagon socket screws of rod type, the steel utilization rate is only 25% to 35% by cutting method, while by cold heading (extrusion), its utilization rate can be as high as 85% to 95%, which is only some process consumption of material head, material tail and cutting hexagonal head edge.
High productivity. Compared with general cutting processing, the efficiency of cold heading (extrusion) is more than dozens of times higher.
Good mechanical properties. The strength of parts processed by cold heading (extrusion) method is much better than that of cutting processing because the metal fiber is not cut off.Suitable for automated production. Fasteners (including some special-shaped parts) suitable for cold heading (extrusion) method are basically symmetrical parts, suitable for production by high-speed automatic cold heading machine, and also the main method of mass production.
In short, the cold heading (extrusion) method for processing fasteners and special-shaped parts is a processing method with a very high comprehensive economic benefit. It is a processing method commonly used in the fastener industry. It is also an advanced processing method that is widely used and has great development both at home and abroad.
Cold heading, cold pressing:
At room temperature, the blank is placed in the mold of an automatic cold heading machine or a press, and pressure is applied to the mold. The relative movement of the upper and lower molds is used to deform the blank in the mold cavity, reduce the height, and increase the cross section. This pressure processing method is called cold heading for automatic cold heading machines and cold pressing for presses. In actual production, the cold forming process of fasteners is often accompanied by extrusion during the cold heading process. Therefore, the cold heading process of fastener products is actually a composite processing method that has both cold heading and extrusion.
Deformation methods of cold heading (extrusion):
1. Punching. Separate part of the blank from the main body, such as cutting of wire, punching of nuts, trimming of the head of hexagonal bolts, etc.
2. Upsetting. A processing method that shortens the height of the blank and increases the cross-section, such as ball upsetting of nuts, pre-upsetting and fine upsetting of bolt head forming, etc.
3. Positive extrusion. During cold heading, when the blank is deformed in the lower die, the flow direction of the metal is consistent with the movement direction of the upper die. The reduction of the thick rod in cold heading bolts and cylindrical head hexagon socket screws is a positive extrusion.
4. Reverse extrusion. During the deformation of the blank, the flow direction of the metal is opposite to the movement direction of the upper die. The head forming of the cylindrical head hexagon socket screw belongs to reverse extrusion.
5. Compound extrusion. During the deformation of the blank, part of the metal flow direction is the same as the movement direction of the upper die, and part is opposite to it, that is, there is both positive extrusion and negative extrusion during the deformation. For example, the cylindrical head hexagon socket screw has both rod diameter reduction (positive extrusion) and head forming (negative extrusion) during the deformation at the same station.
Degree of cold upsetting (extrusion):
Deformation degree refers to the ratio of the compression of the length of the upsetting part of the billet at the end of upsetting to the original height, or the ratio of the increase in the cross-sectional area of the billet at the end of upsetting to the original cross-sectional area. The upsetting ratio can determine the difficulty of upsetting. The smaller the upsetting ratio, the smaller the deformation and the easier the deformation. The larger the upsetting ratio, the more difficult the deformation, the irregular flow of metal fibers, and some fibers are bent, forming a longitudinal bending phenomenon.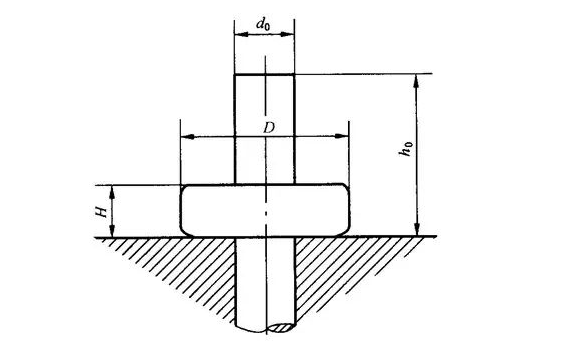
When the degree of cold heading deformation exceeds the deformation limit of the metal itself, cracks will appear on the side of the deformed workpiece, resulting in defective products. The strength of the mold will also be affected, reducing the service life. In severe cases, the mold may crack and be damaged.
The allowable deformation degree of the metal is related to the plasticity of the metal itself. The allowable deformation degree of metal with good plasticity is higher than that of metal with poor plasticity. The higher the carbon content of carbon steel, the lower its plasticity and the smaller the allowable deformation degree. In production, for metals with poor plasticity, such as medium carbon steel and alloy steel, cold heading often adopts annealing and softening treatment of the steel, increasing the toughness of the mold, and lubricating the metal surface, etc., in order to increase the allowable deformation degree of the metal. Table 1 lists the allowable deformation degree of some steels.
